Must-Know QR Code History Facts: From 1994 to the Present

The QR code history showcases a remarkable journey of technological advancement.
Originally developed as a tracking tool for automobile parts, these codes have since become a staple in modern communication, fundamentally changing how we engage with digital content.
This article highlights the major milestones and developments that have shaped the growth of QR codes, exploring the evolution of how this simple technology has reshaped industries and enhanced everyday experiences today.
Table of Contents
Get to know the basics of what QR codes are
Before we delve into the facts about QR code history, let's briefly define the technology and answer the most common questions about how do QR codes work and how to use them effectively.
Quick Response (QR) code is a scannable, two-dimensional barcode designed for digital devices like smartphones, which now come with a built-in QR code scanner.
It’s a grid of dark or light pixels that encodes information, serving as a digital bridge linking the physical world to the online realm.
QR codes are commonly used to track products in supply chains and in mobile-first marketing and advertising campaigns.
In fact, QR TIGER QR Code Generator's 2024 QR code trend report shows a 323% growth in QR code usage in marketing and advertising.
While QR technology might seem like a recent innovation, its origins actually run deeper. Before the existence of these codes, there were other machine-readable codes, such as the Universal Product Code (UPC) found on grocery items.
However, QR codes offered a significant improvement by storing much more data in a compact space, making them the ideal choice for various applications.
If you're wondering where did QR codes originally come from and how they evolved, let's explore their fascinating development timeline and discover how these ubiquitous codes came to be.
QR code history: A chronological timeline

The journey of QR codes from their inception to their widespread use today is a remarkable story of technological innovation and adaptation. Let’s get to know the roots and history of how it came to be:
1960: Pre-QR code era
The 1960s witnessed a surge in consumerism, particularly in Japan, leading to the rapid expansion of supermarkets.
The overwhelming number of products posed a significant challenge for cashiers, who had to manually enter prices for each item. This repetitive task often led to physical strain and errors, hampering efficiency.
Although machine-readable codes were available at the time, their complexity and high costs rendered them impractical for small and medium-sized businesses, highlighting the need for a more efficient and affordable solution.
This period saw the emergence of barcodes. In 1952, American engineers Norman Woodland and Bernard Silver patented a linear scanning technology system.
Their original design, resembling a bullseye, laid the foundation for modern barcodes. However, this innovative technology remained largely unused for the next two decades.
In the U.S., the post-war supermarket boom created an urgent demand for a faster and more accurate method of processing products at checkout.
In collaboration with the grocery industry, IBM revisited the earlier patented technology and developed the vertically aligned UPC barcode we recognize today.
1970: Barcode adoption
The 1970s marked a transformative period in retail technology with the advent and rapid adoption of the barcode.
IBM developed this machine-readable code to address the growing challenges in inventory management and checkout efficiency, transforming the industry.
Created by IBM engineer George Laurer, the barcode offered a significant leap over existing systems, enabling quicker and more accurate product identification.
Its ability to streamline checkout and lighten the load for cashiers led to its rapid acceptance in supermarkets and other retail spaces.
A major breakthrough occurred in 1973 when George Laurer invented the UPC, a square barcode specifically designed for retail.
Easily scanned by optical readers, the UPC's adoption by a consortium of grocery companies signaled the start of barcode-based scanning, which will transform product tracking and processing at the point of sale (POS).
This vertically aligned system encoded a unique 12-digit number that could be swiftly scanned by a laser beam, making product identification and processing more efficient.
This innovation improved retail operations and set the stage for the future development of more advanced barcode technologies.
1994: The rise of QR codes
While barcodes were a significant advancement, their limitations became apparent over time.
With their limited storage capacity, they struggled to meet the demands of more complex applications.
This led to the invention of QR codes. Have you ever wondered who invented the QR code?
In 1994, Denso Wave, a Japanese manufacturing technology company, set out to develop a more versatile machine-readable code.
Their efforts resulted in the development of QR codes, a two-dimensional code capable of storing far more data than traditional barcodes.
Originally intended for industrial use, QR codes quickly became popular due to their flexibility. They can be easily created using a QR code generator available online.
They can store text, URLs, contact information, and much more, proving invaluable in marketing, event management, and supply chain tracking.
While UPC barcodes have transformed the grocery industry, their storage and scanning speed limitations have become drawbacks.
The introduction of the QR codes offered a substantial upgrade, with the ability to hold more data, scan faster, and be read from various angles and distances.
2000: Global adoption
The early 2000s marked a significant turning point in QR code history. As smartphones gained popularity, QR codes became widely accessible to the public.
Mobile apps that could easily scan and interpret these codes further propelled their use, leading to their integration into payments, event ticketing, social media, and authentication.
Today, QR codes are a common sight, and World QR Code Day is celebrated to honor their widespread use and impact.
This annual event showcases the technology's versatility and its contributions across different industries. It highlights the innovation behind QR codes and explores future possibilities.
2010: Rise to global popularity
By 2010, QR codes had gained worldwide popularity, appearing in industries such as retail, events, and advertising.
Consumers could swiftly scan them to access product details, download apps, or even complete payments.
The arrival of dynamic QR codes, which could be updated without changing the physical code, broadened their applications.
This innovation enabled time-sensitive promotions, personalized content, and real-time tracking.
QR codes also transformed mobile payments, especially in Asia, where they became a common payment method used everywhere, from street vendors to luxury department stores in countries like China and Japan.
2020: Significance to the COVID-19 fight

The widespread adoption of QR codes during the COVID-19 pandemic has dispelled any notion of whether Are QR codes dead or Do they still have use.
Businesses and organizations embraced QR codes to offer menus, facilitate contactless payments, and share essential information, all in an effort to curb the virus's spread.
During this time, QR codes emerged as a symbol of safety and convenience, helping consumers minimize physical contact and lowering the transmission risk.
Governments and healthcare organizations also use QR codes to trace contacts, verify vaccine records, and distribute health information.
2020 to present: Omnichannel innovations
As technology advances, the potential of QR codes expands with it.
In recent years, innovation in QR codes has soared, introducing different types of QR codes and solutions, custom designs, augmented reality integration, and enhanced security features.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is bridging the gap between physical objects and the digital world, with QR codes playing an important role in this shift.
GS1, the global standards organization, has also been key in promoting QR codes for supply chain management and product traceability.
By adopting GS1 standards, businesses can achieve greater interoperability and efficiency in their QR code usage.
The technology is set to become even more integral to our lives. The codes’ versatility and ease of use have made them popular with individuals and businesses around the world.
Global adoption and expansion of QR codes

Looking at the QR code timeline, the technology first gained traction in Japan and has since seen widespread adoption in China, the United States, Europe, and other countries.
The rise of smartphones and the creation of QR code-enabled apps have been key drivers in their global spread. Here are some additional QR code facts backed by statistical findings:
The growing popularity of QR codes: Statistical insights
QR codes have seen a dramatic rise in usage and industry adoption globally.
Statista reports that between 2022 and 2025, the number of US consumers scanning QR codes with smartphones will increase by 16 million.
This growth is fueled by the rise of contactless payments, mobile marketing, and greater consumer familiarity with the technology.
The QR code payment market has also expanded rapidly. Allied Market Research forecasts it will hit USD 35.07 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 16.1%.
This growth is driven by the growing popularity of mobile payments, especially in developing nations, and the convenience and security of QR code transactions.
To illustrate the widespread adoption of QR codes, consider the following statistics:
- Search volume: Ahrefs reports a global search volume of 2.5 million for "QR Code," showing substantial interest and awareness.
- Consumer usage: A large percentage of mobile users are actively scanning QR codes. Business Wire reports that 84% of mobile users have scanned a QR code at least once, and 72% do so at least once a month.
- Industry adoption: Future Market Insights indicates that QR codes are being integrated across sectors such as retail, hospitality, healthcare, and education.
The QR code labels market is expected to reach $2.1 billion by 2027, reflecting the growing demand for this technology.
Key advantages of using QR codes
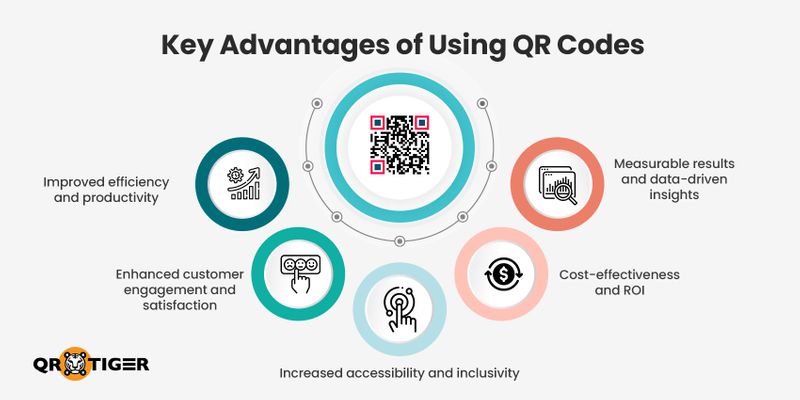
Let’s explore the key benefits of QR codes and their impact across various industries:
Improved efficiency and productivity
One of the most significant advantages of QR codes is their ability to streamline processes and boost efficiency.
With a quick scan, individuals can instantly access information, complete payments, or interact with digital content, cutting out the need for manual data entry or searching.
This saves both time and effort. Businesses can use QR codes to automate tasks like inventory management, employee check-ins, and customer data collection.
Enhanced customer engagement and satisfaction
Want to give your customers a special experience? Incorporating QR codes into marketing materials allows businesses to engage customers in a unique, personalized way.
These codes can guide customers to exclusive offers, behind-the-scenes content, or interactive experiences, fostering brand loyalty and boosting customer satisfaction.
Additionally, QR codes provide a valuable tool for gathering customer feedback and preferences, enabling businesses to customize their products and services to meet specific needs.
Increased accessibility and inclusivity
QR codes can make information and services more accessible to a broader audience.
For instance, QR codes can deliver audio descriptions for visually impaired individuals or provide translated content for those who speak different languages.
This approach fosters inclusivity, ensuring everyone can benefit from the available information or services.
Cost-effectiveness and ROI
Creating and implementing QR codes might involve some initial costs, but the long-term benefits often outweigh them.
QR codes offer a cost-effective method to reach a broad audience and can deliver a measurable return on investment (ROI).
By monitoring QR code scans and analyzing customer behavior, businesses can gather valuable insights into their marketing strategies and make informed, data-driven decisions.
Measurable results and data-driven insights
QR codes provide a powerful tool for tracking and evaluating the success of marketing campaigns and other initiatives.
Businesses can gather essential insights into customer behavior, demographics, and preferences by analyzing QR code scans.
These insights enable businesses to optimize marketing strategies, enhance customer satisfaction, and make data-driven decisions.
QR TIGER: The best partner for all QR code needs
The QR code history is a testament to the ingenuity and adaptability of human innovation. Once a simple tool for tracking industrial products, they have grown into symbols of the digital age.
Its compact, machine-readable format allows it to store extensive information, making it essential for both businesses and individuals.
QR codes will likely become even more integral to our lives, introducing new ways to connect, communicate, and access information.
With the rise of an advanced and reliable QR code generator like QR TIGER, creating these codes is now easier than ever and accessible to anyone with a smartphone or computer.
The QR code's evolution from a niche technology to a global communication gateway highlights its versatility and adaptability, ensuring its ongoing relevance in the future.
Frequently asked questions
Who invented QR code payment?
QR codes for payment didn’t come from one individual but rather from the fusion of QR codes and mobile payment systems. Its development and popularity resulted from contributions by multiple entities.
Who is the father of QR code?
Masahiro Hara is considered the father of the QR code. He invented it in 1994 while working on a project to improve efficiency in a manufacturing setting
Where can I find the best QR code scanner?
You can find advanced QR scanners in your smartphone's app store. Many popular choices are available for both Android and iOS devices. Simply search for a scanner for QR code and pick one with high ratings.




